2. For points on the equatorial plane :
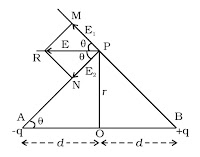
Consider an electric dipole AB. Let 2d be the dipole distance and p be the dipole moment. P is a point on the equatorial line at a distance r from the midpoint O of the dipole (Fig.).
Fig. Electric field at a point on equatorial line & Components
Electric field at a point P due to the charge +q of the dipole,
E1= q / [4πεo (BP^2) ] (along BP)
E1= q / [4πεo (r^2+d^2) ] (along BP) (∵BP^2 = OP^2 + OB^2)
Electric field (E2) at a point P due to the charge –q of the dipole
E2 = q / [4πεo (AP^2) ] (along PA)
E2 = q / [4πεo (r^2+d^2) ] (along PA)
The magnitudes of E1 and E2 are equal. Resolving E1 and E2 into their horizontal and vertical components (Fig.), the vertical components E1 sin θ and E2 sin θ are equal and opposite, therefore they cancel each other.
The horizontal components E1 cos θ and E2 cos θ will get added along PR.
Resultant electric field at the point P due to the dipole is
E = E1 cos θ + E2 cos θ (along PR)
E = 2 E1cos θ ( ∵ E1 = E2 )
E = q / [4πεo (r^2+d^2)] x 2 cos θ
but cos θ = d / (r^2+d^2)^1/2
E = q / [4πεo (r^2+d^2)] x 2 d / (r^2+d^2)^1/2
E = p / [4πεo (r^2+d^2)^3/2] (∵p = q2d)
For a dipole, d is very small when compared to r
E = p / [4πεo r^3]
The direction of E is along PR, parallel to the axis of the dipole and directed opposite to the direction of dipole moment.